2 Setting Up
Setting up your system involves setting up your hardware and installing software on it. This chapter explains how to do both and then provides a sequence of steps and troubleshooting tips to test your setup.
2.1 What You’ll Need
This development kit includes much of the software you will need to write and debug GEOS applications. It does not, however, include a C compiler or the hardware you will need. Make sure you have all of the items on the following lists before proceeding.
2.1.1 Hardware You’ll Need
This kit provides no hardware. To set up your system, you will need at least the following:
Development PC The computer on which you will do your programming is referred to as the Development PC, the Host PC, or occasionally the Workstation. This PC must have an 80386 or more powerful processor and preferably eight or more megabytes of RAM. It should have a hard disk of at least 80 megabytes.
Target PC The computer on which you will run GEOS and on which you will test your applications is referred to as the Target PC or the Test PC. This may be any Intel-compatible PC. Geoworks recommends that you have two test PCs: A powerful machine which you can debug on quickly, and an XT-class machine on which you can test your application’s speed. When this isn’t possible, you should try to have a more powerful machine in order to test various video drivers and memory configurations with your application.
Serial Cable(s) The Host and Target PCs must be connected via serial link. You should keep the machines relatively close together, so a six-foot cable should be adequate.
Null Modem A null modem is required in the serial connection between the host and target PCs. Without it, the send and receive pins on one of the machines will be reversed. Note that Lap-link cable includes this null-modem connection.
Gender Changers and/or Adapters for Serial Cables Depending on the cables and connectors you have, you may need one or more serial line gender changers or other adapters.
2.1.2 Software You’ll Need
As stated above, this kit does not provide all the software you’ll need. Both the host and target machines must be loaded with some version of DOS, and you will also need to have the following:
C Compiler Currently, only Borland C/C++ 3.0 and 3.1 are supported for GEOS development. Geoworks is working on supporting others.
You may also want to use a task-switching environment on the host machine to make switching between coding, compiling, and debugging easier and quicker.
2.2 Setting Up the Hardware
First, set up your two PCs according to their included instructions (if any). Keep in mind that you will be switching frequently between the two machines and that you will often be using the mouse on the target machine while typing on the keyboard of the host machine.
Next, connect the two machines via serial cable and a null modem. Be sure to remember which serial ports you used on both machines, as you will need to know when installing the software. You may need to add in gender changer(s), 9-to-25 pin adapter(s), or other connectors, depending on your machines and your cables. A simplified diagram of the connection is shown in Figure 1-1.
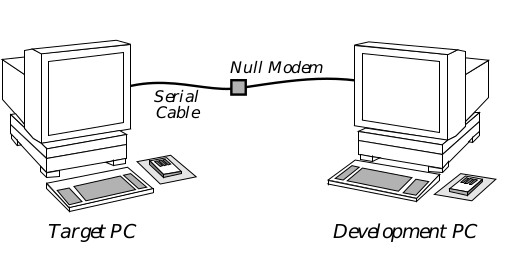
Figure 1-1 Workstation Setup The test and development PCs communicate via a null modem serial connection.
2.3 Installing the Software
Once you have finished setting up your machines and have connected the serial cable, you must install the GEOS development kit. Place the SDK CD-ROM into your CD-ROM drive, change to that drive, and run the INSTALL program.
The installation program will ask questions so it can set up the DOS environment for use with the GEOS development tools. These questions include which COM ports you used to connect the development and test machines. Answering these questions incorrectly can cause the SDK not to function properly.
Important: You must set both machines to use the same baud rate. They may use different COM ports, but they must have the same baud rate.
After you have installed the two disk sets, you must install your C compiler on the host (development) machine (if you have not already done so). Follow the instructions provided with your compiler.
Finally, you should run through the “setup” programs for both the error-checking and the non error-checking versions of GEOS on the target machine. To run the error-checking version, type
C:\>cd geosec
C:\GEOSEC>geosec
This will run GEOS, which will automatically kick into the graphical setup program. This program will ask you your video type, your mouse type, etc. If the setup does not go smoothly, try reinstalling the target disks.
To run the non error-checking setup, type
C:\>cd geosnc
C:\GEOSNC>geos
Again, if the set-up does not go smoothly, try reinstalling the disks. If this does not work, check that you are using the proper hardware configurations. If one or both of the two GEOS directories does not exist, try reinstalling the target disks.
2.4 Testing the Configuration
Once you have finished installing all the software, your system should be ready for you to begin programming. To check it, however, run through the following sequence of steps. You will learn later exactly what these steps do in more detail, but for now it is sufficient just to try them.
Host Machine: cd \pcgeos\appl\sdk_c\hello
On the host machine, change directories:
C:\>cd \pcgeos\appl\sdk_c\hello
If this directory does not exist, check that the \PCGEOS directory exists. If it doesn’t, check which directory you installed into, and try that path instead. If this still doesn’t work, make sure that something has been installed on your hard drive; if nothing has, you should try reinstalling the host disk set.
Host Machine: mkmf
Next, run the “make Makefile” program on the host machine with the mkmf command:
C:\PCGEOS\APPL\SDK_C\HELLO>mkmf
Don't forget to run "pmake depend"
Your directory should now contain a file called MAKEFILE.
- If you get a “Bad command or file name” error, make sure that your path includes C:\PCGEOS\BIN (or C:\DIR\BIN, where DIR is the name of the directory in which you installed the host machine programs).
Host Machine: pmake depend
Next, create a dependencies file with the pmake depend command. The output you get should be similar to that shown below.
makedpnd ENDCMODULES GOC GOC goc -M -D__GEOS__ -IDEPENDS -I. -IC:\PCGEOS\INCLUDE
-IC:\PCGEOS\INCLUDE\ANSI -I- -IDEPENDS -I. -IC:\PCGEOS\INCLUDE
-IC:\PCGEOS\INCLUDE\ANSI -w -cb ENDFLAGS HELLO.GOC ENDFILES CPP BORLAND CPP
-D__GEOS__ -Ot -c -v -y -i200 -ml -I. -IC:\PCGEOS\INCLUDE -IC:\PCGEOS\INCLUDE\ANSI
ENDFLAGS HELLO.C ENDFILES
FILE C:\PCGEOS\INCLUDE\stdapp.goh, line 18 Warning: remaking @optimized file
C:\PCGEOS\INCLUDE\stdapp.goh. Missing depends or pre-goc'ed file
FILE C:\PCGEOS\INCLUDE\object.goh, line 17 Warning: remaking @optimized file
C:\PCGEOS\INCLUDE\object.goh. Missing depends or pre-goc'ed file
FILE C:\PCGEOS\INCLUDE\ui.goh, line 17 Warning: remaking @optimized file
C:\PCGEOS\INCLUDE\ui.goh. Missing depends or pre-goc'ed file
FILE C:\PCGEOS\INCLUDE\iacp.goh, line 22 Warning: remaking @optimized file
C:\PCGEOS\INCLUDE\iacp.goh. Missing depends or pre-goc'ed file
FILE C:\PCGEOS\INCLUDE\gcnlist.goh, line 21 Warning: remaking @optimized file
C:\PCGEOS\INCLUDE\gcnlist.goh. Missing depends or pre-goc'ed file
Processing HELLO.C...
Borland C++ Preprocessor Version 3.1 Copyright (c) 1992 Borland International
hello.c:
Available memory 3563940
findlbdr HELLO.GP DEPENDS.MK HELLO.GEO
C:\PCGEOS\APPL\SDK_C\HELLO>
There should now be a file in your directory called DEPENDS.MK. Don’t worry about those “remaking @optimized file” warnings; these come up when some header files are used for the first time.
- If you get an error like
"makefile". line 13: Could not find GEOS.MK
"LOCAL.MK", line 3: Could not find GEODE.MK
Fatal errors encountered -- cannot continue
you should make sure that your ROOT_DIR variable is set correctly. ROOT_DIR should be the name of whatever directory you installed the host files to. Normally this is C:\PCGEOS.
- If you get the error
C:\PCGEOS\BIN\PMAKE.EXE: Can't figure out how to make DEPEND. Stop
then your makefile was not created correctly. Try running mkmf again to make sure that a makefile is being created.
- If you get the error shown below, you should make sure that you have correctly installed your C compiler, and make sure that your C compiler’s executable is in your path.
makedpnd ENDCMODULES GOC GOC goc -M -D__GEOS__ -IDEPENDS -I.
-IC:\PCGEOS\INCLUDE -IC:\PCGEOS\INCLUDE\ANSI -I- -IDEPENDS -I.
-IC:\PCGEOS\INCLUDE -IC:\PCGEOS\INCLUDE\ANSI -w -cb ENDFLAGS HELLO.GOC
ENDFILES CPP BORLAND CPP -D__GEOS__ -u- -c -v -y -Ot -Oi -i200 -ml -I.
-IC:\PCGEOS\INCLUDE -IC:\PCGEOS\INCLUDE\ANSI ENDFLAGS HELLO.C ENDFILES
Processing HELLO.C...
Depends file removed.
*** Error code 1
Stop.
Host Machine: pmake
Next, make the executable file with the pmake command. The output you should see is shown below.
C:\PCGEOS\APPL\SDK_C\HELLO>pmake
BCC -D__GEOS__ -u- -c -v -y -Ot -Oi -i200 -ml -I. -IC:\PCGEOS\INCLUDE -IC:\PCGEOS\I
NCLUDE\ANSI -oHELLO.OBJ HELLO.C
Borland C++ Version 3.1 Copyright (c) 1992 Borland International
hello.c:
Available memory 3475572
glue -Og HELLO.GP -P 0.0 -R 0.0.0.0 -m -LC:\PCGEOS\INCLUDE\LDF -T 1 -o HELLOEC.GEO
HELLO.OBJ
Resource Size # Relocs
--------------------------------------------------
CoreBlock 0 0
dgroup 144 3
HELLO_TEXT 125 8
INTERFACE 180 1
APPRESOURCE 416 1
Total size: 865 bytes
Uninitialized data/stack: 2000 bytes
Import Number Type Protocol
----------------------------------
geos 0 library 654.000
ui 1 library 741.001
borlandc 2 library 1.000
You should now have a HELLO.GEO file in your current working directory on the host machine. If you do not, try the last few steps again, checking for errors in the output. If there are any, try reinstalling the host disk set and running through this procedure again.
Target Machine: cd \geosec
On your target machine, change to your GEOSEC directory.
Target Machine: pccom
Now, on the target machine, run the pccom tool, which connects the target machine to the host machine.
C:\GEOSEC>pccom
The screen should clear, its background should go dull gray, and the line
waiting for command from remote PC:
should appear at the top in yellow letters. If the pccom tool could not be found, make sure you typed it correctly, and then make sure it is in a directory in your DOS path.
Try typing the Enter key, which should return you to DOS.
- If it does not, then your communication set-up is not configured correctly. Double-check the values of your PTTY variable. If you’re uncertain about the meaning of these values, or how they should be set, you should consult “Troubleshooting Communications,” Appendix A.
Assuming the pccom tool returned you to DOS, run the pccom tool again to get back to the “waiting for command from remote PC” line.
Host Machine: pcs
Return to the host PC. Download the newly-created HELLOEC.GEO file from the host to the target with the following command:
C:\PCGEOS\APPL\SDK_C\HELLO>pcs
sending HELLOEC.GEO to WORLD\C
Your target PC should give output similar to the following:
waiting for command from remote PC:
Receiving: WORLD\C\HELLO.GEO -
File Transfer Complete
waiting for command from remote PC:
If it does not, either HELLOECGEO does not exist (check the earlier steps) or the pccom tool is not working properly. If you get the error message “No matching files,” that means that pcs cannot find your HELLOEC.GEO file. Make sure you did the pmake correctly.
If HELLOEC.GEO exists but pcs still can’t send it to the target machine, then you probably have a problem with your serial connection. Double check the values set in both machines’ PTTY variables. If you aren’t sure what these values should be, or if they look correct, then consult “Troubleshooting Communications”.
If you have successfully gone through the communication troubleshooting procedure and pcs still isn’t working, there’s one more thing you should try: If both machines lock up soon after the “sending HELLOEC.GEO to WORLD\C” message appears, you may be trying to transmit at too high a rate. Reduce the speed of transmission on both the host and target machines. If you’ve already looked through “Troubleshooting Communications,” Appendix A, then you know that you can do this by changing the second field of the PTTY variable or by passing the /b flag to the pccom tool and pcs.
Host Machine: swat
Assuming all has gone well so far, run the debugger now by typing
C:\PCGEOS\APPL\SDK_C\HELLO>swat
The screen should clear after a moment, and the following should come up on the host’s screen:
Swat version 2.0 (Dec 11 1992 13:47:14).
Using the trunk version of PC/GEOS.
Looking for "loader"...C:\PCGEOS/Loader/LOADEREC.EXE
Sourcing swat.tcl...done
PC Attached
Stopped in 0dedh:0007h, address 0dedh:0007h
LoadGeos: CLD ;DF=0
(loader:0) 1 =>
- If you get an error like the following:
Abnormal program termination:Memory protection fault
CS:EIP = 000Fh:0000000Ahof PC/GEOS
then chances are there is a mistake in your CONFIG.SYS file, either on the FILES or BUFFERS line. Your FILES value should probably be at least 80 (at least 100 if you will be task-switching while using Swat). You may note the use of the word “probably” in that last sentence. The third-party memory manager used by Swat has trouble on some hardware set-ups; for these machines, you should try lowering the files number in your CONFIG.SYS to 60 and/or raise the BUFFERS value to 40.
Another possible cause for this sort of error is that your environment variables may be over-running their space. To increase the environment space, make sure there is a line in your CONFIG.SYS file following the pattern:
shell = command.com /e:XXXX /p
where XXXX is a number, 1024 or higher.
- If the only thing that appears on your host machine is
Using the trunk version of PC/GEOS.
and your target machine is frozen (i.e. nothing else appears for at least a minute), you should probably try communicating at a slower rate. Try changing the PTTY variables to use lower values (such as 9600, if you are trying with 19200). Remember that the value should be the same on both machines.
Host Machine: c
If everything has gone well up to this point, then type “c” at the Swat shell prompt.
(loader:0) 1 => c
Looking for "geos Eker"...C:/PCGEOS/Library/Kernel/geosec.geo
Looking for "ms4 Eifs"...C:/PCGEOS/Driver/IFS/DOS/MS4/ms4ec.geo
Thread 1 created for patient geos
Thread 2 created for patient geos
Looking for "vidmem Edrv"...C:/PCGEOS/Driver/Video/Dumb/VidMem/vidmemec.geo
Looking for "swap Elib"...C:/PCGEOS/Library/Swap/swapec.geo
Looking for "xms Edrv"...C:/PCGEOS/Driver/Swap/XMS/xmsec.geo
Looking for "disk Edrv"...C:/PCGEOS/Driver/Swap/Disk/diskec.geo
Looking for "kbd drvr"...C:/PCGEOS/Driver/Keyboard/kbd.geo
Looking for "nimbus Edrv"...C:/PCGEOS/Driver/Font/Nimbus/nimbusec.geo
Looking for "stream Edrv"...C:\PCGEOS/Driver/Stream/streamec.GEO
Looking for "sound Elib"...C:/PCGEOS/Library/Sound/soundec.geo
Looking for "standardEdrv"...C:/PCGEOS/Driver/Sound/Standard/standard.geo
Looking for "ui Elib"...C:/PCGEOS/Library/User/uiec.geo
Thread 0 created for patient ui
Looking for "styles Elib"...C:\PCGEOS/Library/Styles/stylesec.GEO
Looking for "color Elib"...C:\PCGEOS/Library/Color/colorec.GEO
Looking for "ruler Elib"...C:\PCGEOS/Library/Ruler/rulerec.GEO
Looking for "text Elib"...C:/PCGEOS/Library/Text/textec.geo
Looking for "motif Espu"...C:\PCGEOS/Library/Motif/motifec.GEO
Looking for "vga Edrv"...C:/PCGEOS/Driver/Video/VGAlike/VGA/vgaec.geo
Looking for "nonts Edrv"...C:/PCGEOS/Driver/Task/NonTS/nontsec.geo
Looking for "spool Elib"...C:\PCGEOS/Library/Spool/spoolec.GEO
Thread 0 created for patient spool
Thread 0 created for patient spool
Looking for "serial Edrv"...C:/PCGEOS/Driver/Stream/Serial/serialec.geo
Looking for "msSer Edrv"...C:/PCGEOS/Driver/Mouse/MSSer/msserec.geo
Looking for "welcome Eapp"...C:/PCGEOS/Appl/Startup/Welcome/welcomee.geo
Thread 0 created for patient welcome
- If you get the following sorts of errors (this will occur after a fair amount of normal Swat output)
Looking for "sound Elib"...C:/PCGEOS/Library/Sound/soundec.geo
Looking for "standardEdrv"...hmmmm.
Can't find executable file for "standardEdrv" (version mismatch?)
Answer "quit" to exit to the shell
Answer "detach" to detach and return to top level
Answer "ignore" to ignore this patient
Where is it? C:\PCGEOS\APPL\SDK_C\HELLO/
then your FILES value in your CONFIG.SYS file may be set too low. Try changing this value to something higher (it should probably be at least 80 for most users, at least 100 if you will be using Swat while task-switching). You may note the use of the word “probably” in that last sentence. The third-party memory manager used by Swat has trouble on some hardware setups; for these machines, you should try lowering the files number in your CONFIG.SYS to 60 and/or raise the BUFFERS value to 40.
- If you get the following error:
Looking for "geos Eker"...c:/pcgeos/Library/Kernel/geosec.geo
Interrupt 13: Protection violation
Stopped in 3328h:2a6dh, address 3328h:2a6dh
Swat+10861: CALL Swat+4114
(geos:0)
Then interrupts on your target machine are interfering with interrupts which Swat uses to communicate between machines. Exit the pccom tool on the target machine (if you encounter this error, chances are you will need to restart your target machine), and make sure that from now on you call the pccom tool with the /i:d flag. This will ask the pccom tool to ignore spurious interrupt 13 signals (d is 13 in hex). To do this, create a file called COMM.BAT on the target machine with the following contents:
pccom /i:d
From now on, whenever you would normally invoke the pccom tool on the target machine, just use comm instead.
Host Machine: quit
When you can get through all of those steps without hitting any errors, your setup is probably in good working order.
To exit from Swat (so that you can go on to other things), type quit at the Swat prompt. You may need to enter the DOS command cls to reset your screen after exiting Swat.